Validation of drug delivery could soon be provided by PET imaging tracking of liposomal nanomedicines
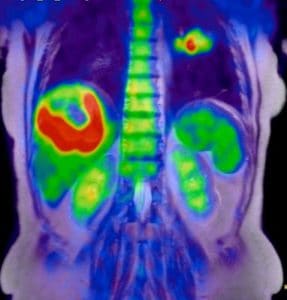
Validation of drug delivery could soon be provided by PET tracking of liposomal nanomedicines, according to a new study published on October 26th, 2016 in ACS Nano.
Researchers have been developing the method at King’s College London in the U.K., Shaare Zedek Medical Center in Jerusalem, Israel, and many other institutions. The PET radio-labeling exploits the metal-chelating properties of certain drugs such as alendronate and doxorubicin, as well as ionophores, in order to achieve excellent radio-labeling yields, purities, and stabilities with 89Zr, 52Mn, and 64Cu, and without needing to modify the nanomedicine components.
The drugs accumulate in tumors and metastatic tissues in varying therapeutic concentrations, and in most cases, at levels well above those in normal tissues, according to imaging with PET in mouse models of breast and ovarian cancer. The nanomedicines unexpectedly showed up in the uterus in one mouse strain, and would not have been detected without the PET imaging study.
Get Started
Request Pricing Today!
We’re here to help! Simply fill out the form to tell us a bit about your project. We’ll contact you to set up a conversation so we can discuss how we can best meet your needs. Thank you for considering us!
Great support & services
Save time and energy
Peace of mind
Risk reduction
“This technique allows quantification of the biodistribution of a radio-labeled stealth liposomal nanomedicine containing alendronate that shows high uptake in primary tumors and metastatic organs,” concluded senior author Rafael Torres Martin de Rosales, PhD, of KCL, and colleagues. “The versatility, efficiency, simplicity, and GMP compatibility of this method may enable submicrodosing imaging studies of liposomal nanomedicines containing chelating drugs in humans, and may have clinical impact by facilitating the introduction of image-guided therapeutic strategies.”
Chelation is the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and the single central atom of a metallic ion. Ligands are usually organic compounds known as chelants or chelating agents. Chelation delivers nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast agents in MRI and PET scanning, in manufacturing using homogenous catalysts, and in fertilizers.